-
[Coursera] Stanford Machine LearningStudy/Coursera 2020. 8. 22. 13:49반응형

01. Introduction
Machine Learning
- Grew out of work in AI
- New capability form computers
Examples
- Database mining
- Large datasets from growth of automation/web.
- E.g., Web click data, medical records, biology, engineering
- Applications can't program by hand.
- E.g., Autonomous helicopter, handwriting recognition, most of Natural Language Processing(NLP), Computer Vision.
- Self-cusomizing programs
- E.g., Amazon, Neflix product recommendataions
- Understanding human learning (brain, real AI)
02. What is machine Learning
Machine Learning definition
- Arthur Samuel (1959)
Machine Learning: Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.
- Tom Mitchell (1998)
Well-posed Learning Problem: A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some
task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.Machine learning algorithms:
- Supervised learning
- Unsupervised learning
- Others: Reinforcement learning, recommender systems.
03. Supervised Learning

- "right answers" given
Regression (회귀)
- Predict continuous valued output(price)
- 연속적인 결과값을 예측

Classification (분류)
- Discrete valued output (0 or 1)
- 0 또는 1, 양성인지 악성인지 등과 같이 불연속적인 결과값을 예측

04. Unsupervised Learning

- 클러스터링 알고리즘 (ex 구글 뉴스)

- 비지도 학습의 예
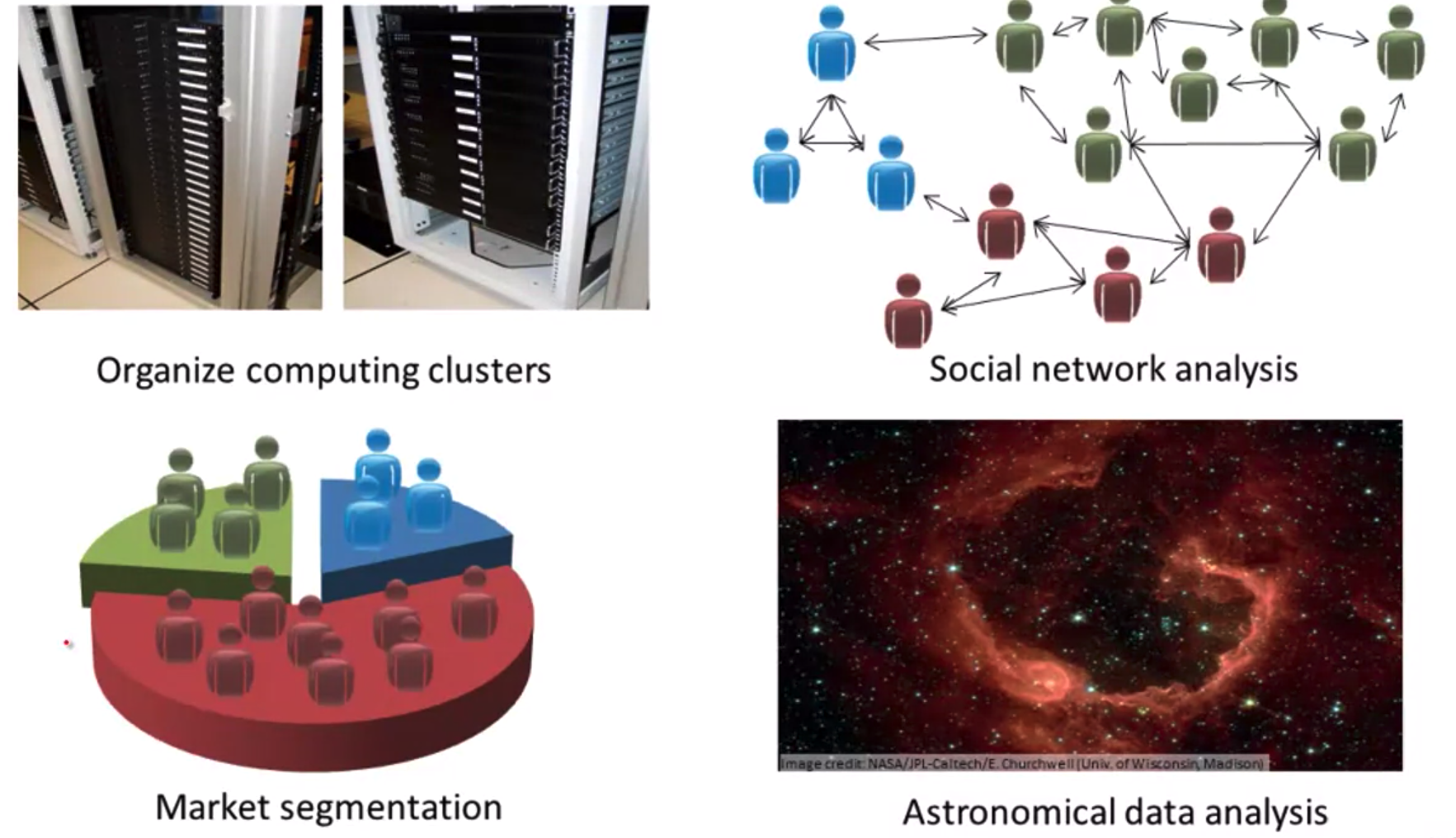
- Orhanize computing clusters
- Social network analysis
- Market segmentation
- Astronomical data analysis
Cocktail party problem

- 두 개의 소리가 녹음된 마이크에서 하나의 소리를 분리해내는데는 단 한 줄의 코드면 충분하다.

Octave
- Octave나 Matlab 같은 도구를 사용하면 많은 학습 알고리즘을 몇 줄의 코드로 구현할 수 있다.
05. Linear regression with one variable Model representation
- 집세에 대한 예측 (Housing Prices)

- Supervised Learning
- Given the "right answer" for each example in the data.
- Regression Problem
- Predict real-valued output
- Classification
Training set (학습 데이터)

- Notation
- m = Number of training examples
- x's = "input" variable / features
- y's = "output? variable / "target" varaible
- (x, y) - one training example
- (x(i), y(i)) - i th training example
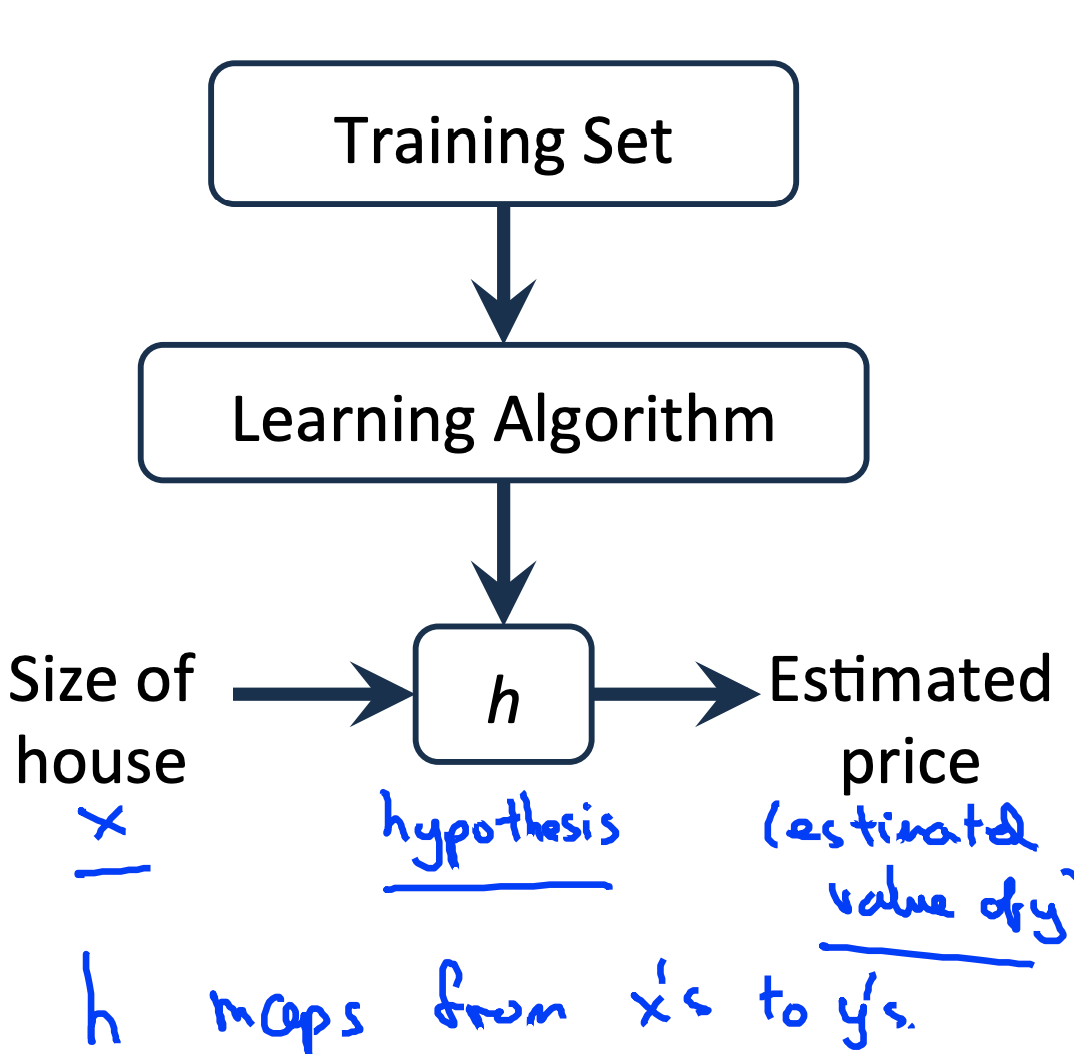
선형회귀
- 단일변량 선형회귀
- 단일변량 : 하나의 값

Cost function (비용함수)
- We can measure the accuracy of our hypothesis function by using a cost function.
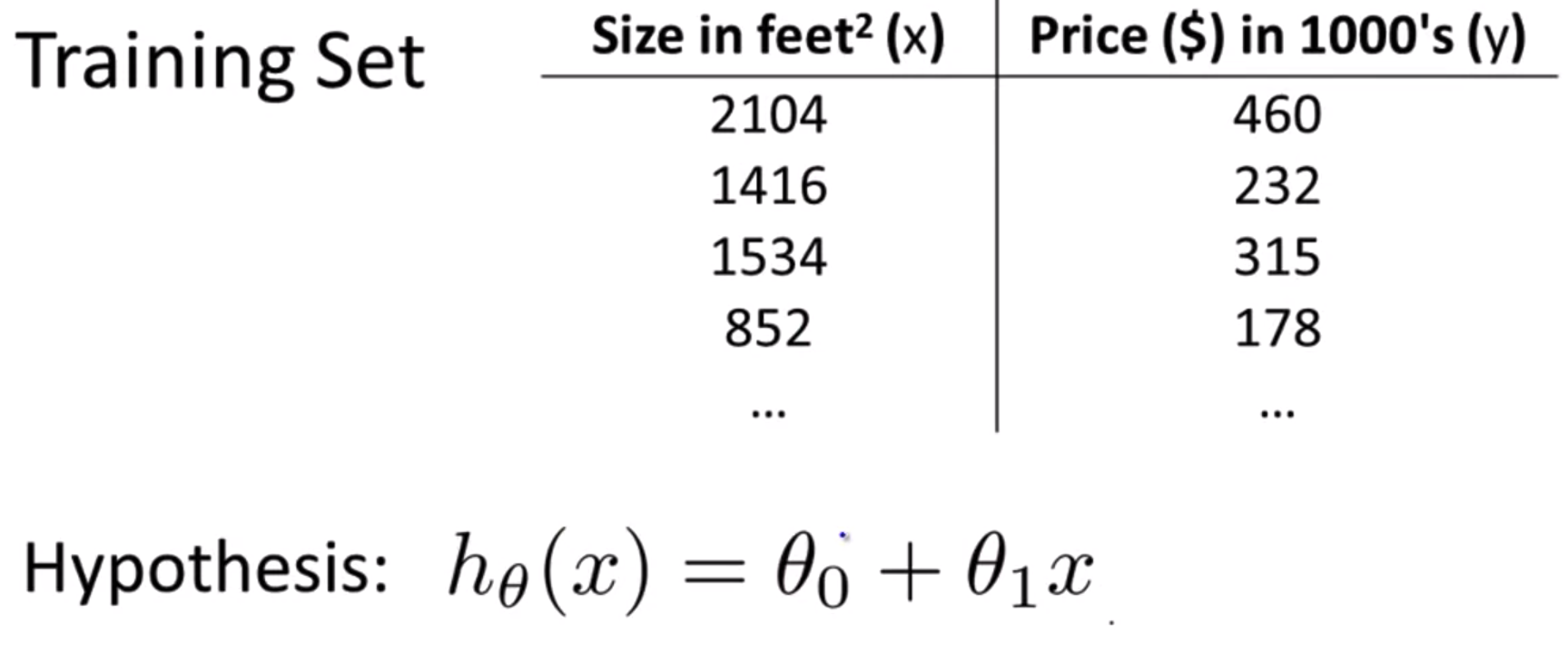

- 비용함수를 사용하면 주어진 데이터에 가장 가까운 일차함수 그래프를 알아낼 수 있다.

- 이 함수를 "제곱 오차 함수" 또는 "평균 제곱 오차"라고 한다.
Cost Function - Intuition I

Cost Function - Intuition II

Gradient descent
- 기울기 하강은 기계학습의 모든 곳에서 실제로 사용되고 있음
- 비용함수 j의 최소값을 구하는 알고리즘
반응형'Study > Coursera' 카테고리의 다른 글
Harvard CS50_ASCII 코드 (0) 2018.10.06 Harvard CS50_2진수 (0) 2018.10.05 Harvard CS50_비트와 바이트 (0) 2018.09.28 Harvard CS50_기억장치 (0) 2018.09.23 Harvard CS50_하드웨어 (0) 2018.09.09